Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding where your visitors are coming from is the foundation of a successful SEO strategy, and one of the most critical segments is organic traffic. This guide will walk you through how to check organic traffic in GA4 (Google Analytics 4), the newer, more feature-rich version of Google Analytics.
What Is Organic Traffic?
Visitors finding your site through non-paid search results constitute organic traffic. Essentially, these are the users who find your content naturally by typing queries that your pages rank for.
Why Is Organic Traffic Important for SEO?
Organic traffic is often considered the most valuable type of traffic because it indicates that your SEO efforts are working. Higher organic traffic means that your website is performing well in search engine rankings, leading to more visibility, brand awareness, and conversions.
Discover the power of organic traffic for SEO today!!
Our specialists explain how organic traffic boosts your SEO performance for higher visibility and engagement online!
GA4 vs. Universal Analytics: What’s New?
If you’ve been using Universal Analytics, you’ll notice some changes when it comes to tracking traffic in GA4. Key differences include enhanced event tracking, improved cross-device measurement, and artificial intelligence-powered insights. Additionally, GA4 introduces a more flexible and customizable data model, allowing for better alignment with modern web and mobile tracking requirements.
Differences in Traffic Reporting
One of the main differences is the way data is structured and reported. GA4 uses event-based tracking rather than the session-based tracking of Universal Analytics. This means more detailed and flexible reports but also a steeper learning curve for those used to the older interface.
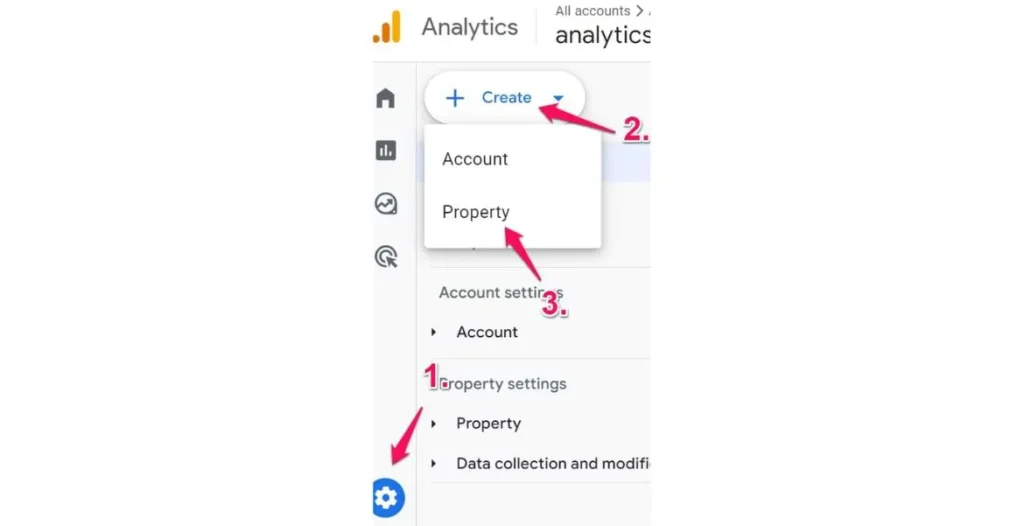
Setting Up GA4 for Organic Traffic Tracking
Before you can view organic traffic, you need to ensure your GA4 account is properly configured. This includes setting up the Google Analytics 4 tag, enabling the Organic Search option, and configuring your data stream to capture search engine traffic, allowing for accurate attribution and insights into your website’s search engine optimization (SEO) effectiveness.
Account Setup and Initial Configuration
- Create or upgrade to GA4 – If you haven’t already set up GA4, you can upgrade your Universal Analytics property.
- Add your website – Ensure your website’s tracking code is properly installed.
- Configure data streams – This is where your website or app data will flow into your GA4 property.
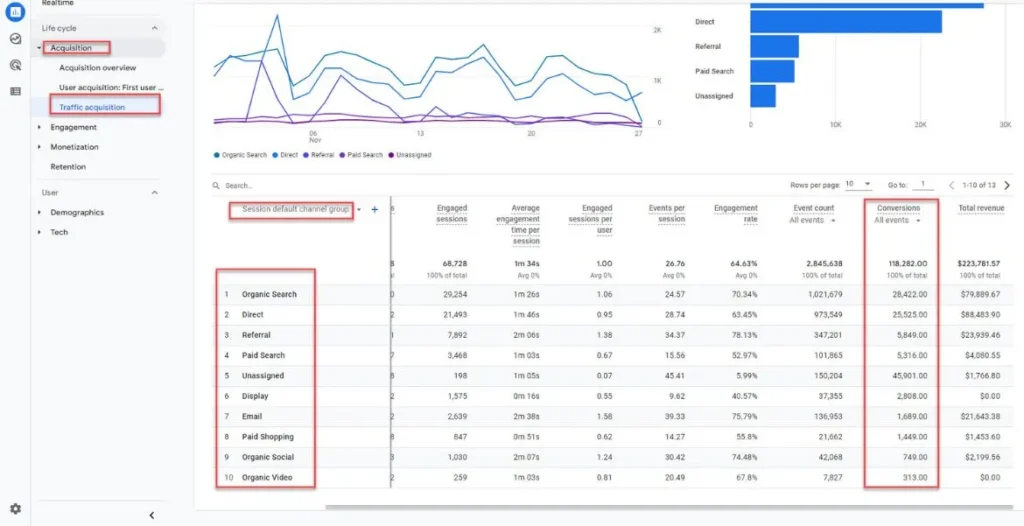
How to View Organic Traffic in GA4?
Step-by-Step Guide to Accessing Organic Traffic Reports
- Log into GA4: Head over to your Google Analytics account and select the GA4 property for your website.
- Navigate to Reports: On the left sidebar, click on “Reports.”
- Click on Acquisition: Under the “Acquisition” section, select “Traffic Acquisition.”
- Filter by Source/Medium: Look for the “Source/Medium” section to filter traffic from organic search engines like Google.
Traffic Acquisition Report: Your Key to Organic Traffic Insights
Access organic traffic metrics and more in GA4’s comprehensive Traffic Acquisition Report. This report provides actionable data on user acquisition, behavior, and conversion, enabling you to refine your SEO strategy, optimize content, and boost website visibility, driving targeted traffic and improving overall digital marketing performance.
Exploring the Source/Medium Dimensions
The Traffic Acquisition Report in GA4 allows you to analyze traffic sources using the Source/Medium dimension. Inspect organic traffic patterns with “Google/Organic” source/medium combination. This combination provides a precise view of your organic search visitors, enabling you to:
- Identify the share of organic traffic from Google
- Measure organic search visitor interaction with your content
- Analyze changes in organic traffic trends over time
- Compare organic traffic to other acquisition channels
You will get the insights into your organic search outcomes by segmenting your traffic data using the Source/Medium dimension.
Filtering for Organic Traffic
Use “Organic” medium to segment natural search traffic. This will isolate the traffic coming from unpaid search results.
Customizing Your Organic Traffic Report in GA4
GA4 offers significant customization options, allowing you to tailor your reports to better meet your SEO needs. With customizable dimensions, metrics, and segments, you can create targeted reports that focus on specific aspects of organic traffic, such as keyword performance, landing page analysis, or device-specific engagement.
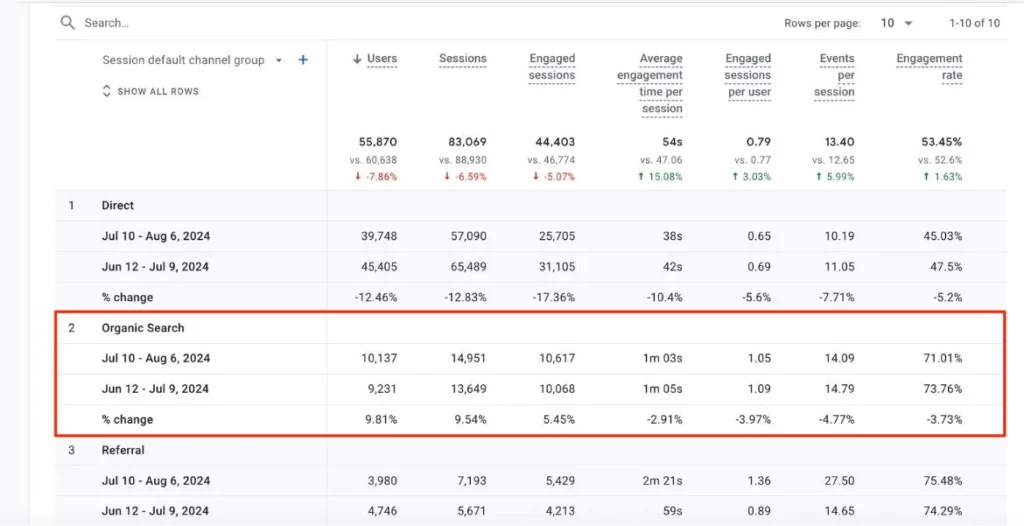
Adding New Dimensions
Want more detail? Add new dimensions to dive deeper into your organic traffic data like:
- User Type
- Landing Page
- Country
Using Filters to Focus on Organic Search
Refine your report by adding filters to focus specifically on organic traffic, and exclude other traffic sources like referrals or paid campaigns.
How to Integrate Google Search Console with GA4 for Deeper Insights?
Integrating Google Search Console with GA4 gives you even more valuable data about your organic traffic, particularly search queries and rankings.
Benefits of Google Search Console Integration
By linking Search Console, you can view search performance metrics, like impressions, clicks, and average position, directly in GA4. Get a clear understanding of your SEO performance and top-performing pages.
Analyzing Landing Page Performance for Organic Traffic
One way to gauge how well your SEO strategy is working is by analyzing the performance of your landing pages. These are the pages that users first see when they arrive via an organic search.
Why Landing Pages Matter in SEO Reporting?
Landing page performance is critical because it shows how well your pages are optimized for search intent and how users engage with them.
GA4 Default Channel Grouping: Understanding Organic Traffic Segments
GA4 categorizes traffic into default channel groupings, with Organic Search being one of the primary segments. This categorization enables accurate attribution and analysis of organic traffic, allowing you to measure the effectiveness of your search engine optimization (SEO) efforts and refine your content strategy.
How Organic Search Fits into Default Channels?
Organic search is listed under default channel groupings in GA4, and by filtering, you can narrow down the data to only show organic traffic. Additionally, GA4’s customizable channel groupings allow you to create tailored segments, providing deeper insights into specific search engines, keywords, or landing pages.
Using GA4 for SEO: Best Practices
GA4 isn’t just about just tracking your site performance; it’s a powerful tool for improving your SEO strategies for your site’s better performance.By harnessing GA4’s advanced analytics capabilities, you can refine your content optimization, technical SEO, and link-building strategies, ultimately driving more qualified organic traffic and boosting search engine rankings.
Tracking Keywords and Organic Search Queries
While GA4 doesn’t directly show keywords, integrating Google Search Console allows you to track which keywords are driving organic traffic to your site. Additionally, this integration enables you to analyze keyword performance metrics, such as impressions, clicks, and click-through rates (CTRs), providing valuable insights to inform and refine your SEO strategy.
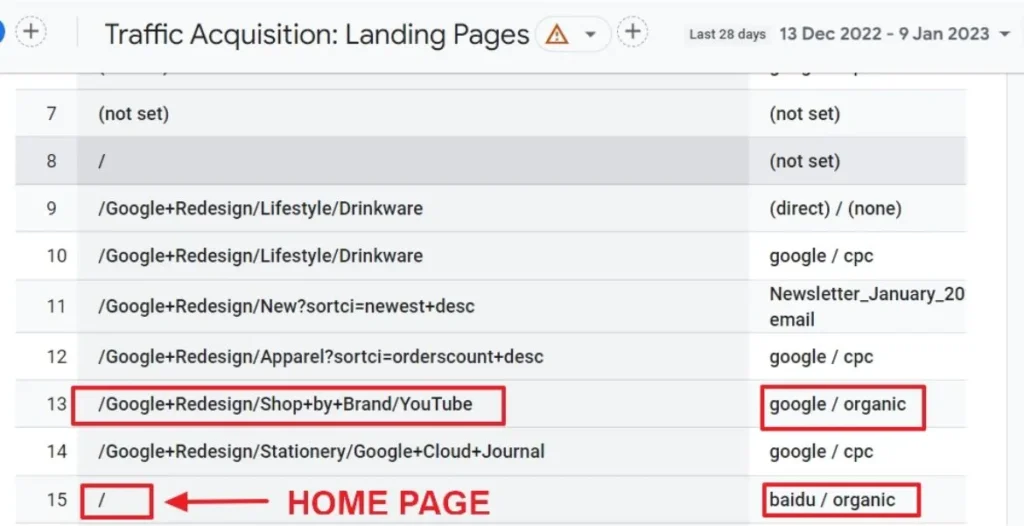
How to Filter Organic Traffic in GA4?
To refine your organic traffic view in Google Analytics, applying a Source/Medium filter is an essential step. This filter enables you to segment and analyze traffic more specifically, ensuring you’re only viewing data from particular sources, such as search engines. Here’s an elaboration on why and how to apply this filter, broken into key points:
1. Understanding Source/Medium
- Source specifies the traffic origin (Google, Bing, websites, etc.)
- Medium refers to the category of traffic, such as organic (unpaid search results), paid (ads), referral (traffic from external sites), or direct (no referral information).
2. Importance of Filtering by Source/Medium
- When you apply a Source/Medium filter for organic traffic, you focus exclusively on traffic that comes from search engines, excluding traffic from other channels.
- This helps you to accurately track the effectiveness of your SEO efforts, understand user behavior, and monitor changes in your organic performance over time.
3. Narrowing Down Organic Traffic Data
- By using a Source/Medium filter, you can:
- Identify search engine traffic from Google, Bing, and others
- Exclude non-organic traffic sources, such as paid campaigns or referrals.
- Analyze organic search behavior and trends without the influence of other mediums like social media or direct visits.
4. Setting Up Source/Medium Filtering in Google Analytics
To apply a Source/Medium filter:
- Access Source/Medium reports via Acquisition > All Traffic.
- In the search bar or filter section, enter the source (like “Google”) and the medium (like “organic”).
- View organic traffic metrics by applying the filter
5. Using Advanced Segments with Source/Medium
- You can create custom segments to track organic traffic across specific search engines or campaigns.
- This segmentation helps in comparing organic traffic with other sources, such as paid or referral traffic, to evaluate marketing strategies.
6. Benefits of Source/Medium Filtering for SEO Analysis
- It provides a clear view of which search engines are driving the most organic traffic.
- Monitor SEO progress with campaign tracking.
- Offers insights into the behavior of organic visitors, including bounce rate, conversion rate, and session duration.
7. Monitoring Organic Traffic Trends
- By regularly applying the Source/Medium filter, you can:
- Track changes in organic traffic over time.
- Identify new opportunities for SEO optimization.
- React to traffic dips or surges based on algorithm updates or changes in user behavior.
8. Focusing on Specific Search Engines
- The Source/Medium filter lets you target data from specific search engines (e.g., Google, Bing) and exclude others if necessary.
- You can compare organic traffic from different search engines to understand which one drives the most valuable users.
By applying Source/Medium filtering, you refine your data to focus exclusively on organic traffic, helping you gain actionable insights for optimizing your website’s SEO performance.
Common Issues When Tracking Organic Traffic in GA4
Misconfiguring filters or data streams can lead to inaccurate tracking. Always double-check your settings to ensure the correct data is being reported. Common GA4 issues include not properly setting up event parameters and neglecting to track all traffic sources, which can skew your organic traffic data. Regularly auditing your GA4 configuration is key to maintaining accurate and reliable reports.
Learn to solve GA4 organic traffic issues today!
Get expert guidance on fixing GA4’s organic traffic tracking errors!
Conclusion
Misconfiguring filters or data streams can lead to inaccurate tracking. Always double-check your settings to ensure the correct data is being reported. Common GA4 issues include not properly setting up event parameters and neglecting to track all traffic sources, which can skew your organic traffic data. Regularly auditing your GA4 configuration is key to maintaining accurate and reliable reports.
FAQs
- How often is GA4 data updated?
GA4 updates its data within 24-48 hours, but some reports may appear sooner. - Can I track organic traffic in real-time?
Yes, GA4 provides real-time data, allowing you to monitor traffic as it happens. - Why does my organic traffic data in GA4 differ from Universal Analytics?
GA4 uses event-based tracking, while Universal Analytics was session-based, leading to potential discrepancies. - Is Google Search Console necessary for organic traffic tracking?
While not mandatory, integrating Search Console provides more in-depth data on search performance. - How do I view organic traffic from different countries?
You can filter organic traffic reports by location using the Country dimension in GA4.





