Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the metrics in Google Analytics can feel like decoding a foreign language at times. One such metric that often raises eyebrows is “event count.” So, what exactly is event count in Google Analytics, and how does it affect your data tracking and reporting? This article will break down everything you need to know about event counts, including how they are used in both Universal Analytics and Google Analytics 4 (GA4). By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of this metric and how to leverage it for better insights into user behavior.
Event Counts in Google Analytics
Google Analytics is packed with features to help you monitor and enhance user interactions on your website. One such tool is the event count, which keeps track of specific user activities—like clicks, form submissions, and video plays. Monitoring these events provides actionable insights into how users engage with your content, helping you improve both the user experience and the effectiveness of your website.
Discover how Event Count boosts your GA4 insights now!
Our experts show you how Event Count helps track user actions effectively!
What Exactly Is an Event Count?
An event count is a measurement of how often users complete certain actions on your website. This could range from clicking a button to submitting a form. Understanding these metrics allows you to gauge user interaction and engagement, ultimately helping you make better decisions for your website.
Difference Between Event Count and Views
Event count refers to the number of specific interactions or actions taken by users on a website, application, or platform. It measures discrete events, such as form submissions, button clicks, purchases, or downloads. Event count provides valuable insights into user behavior, helping analysts understand how users engage with content, features, or calls-to-action. By tracking event counts, businesses can identify areas of high engagement, optimize user experience, and improve conversion rates. For instance, an event count can reveal how many users signed up for a newsletter or completed a survey, allowing businesses to refine their marketing strategies.
Views, on the other hand, represent the number of times content is displayed or loaded, regardless of user interaction. Views measure exposure, counting each instance a page, video, image, or ad is rendered. Views provide insight into content popularity, reach, and visibility. They help analysts gauge the effectiveness of content marketing strategies, track brand awareness, and measure campaign success. For example, view counts can reveal how many times a blog post was displayed, a video was watched, or an advertisement was shown, enabling businesses to refine their content creation and distribution strategies.
Types of Events in Google Analytics
Google Analytics can track a wide array of user interactions, each categorized into different types of events.
Automatically Tracked Events
Certain events are automatically tracked when you set up Google Analytics, such as page views and scroll depth. These basic actions help you get an overview of user activity without needing additional configuration.
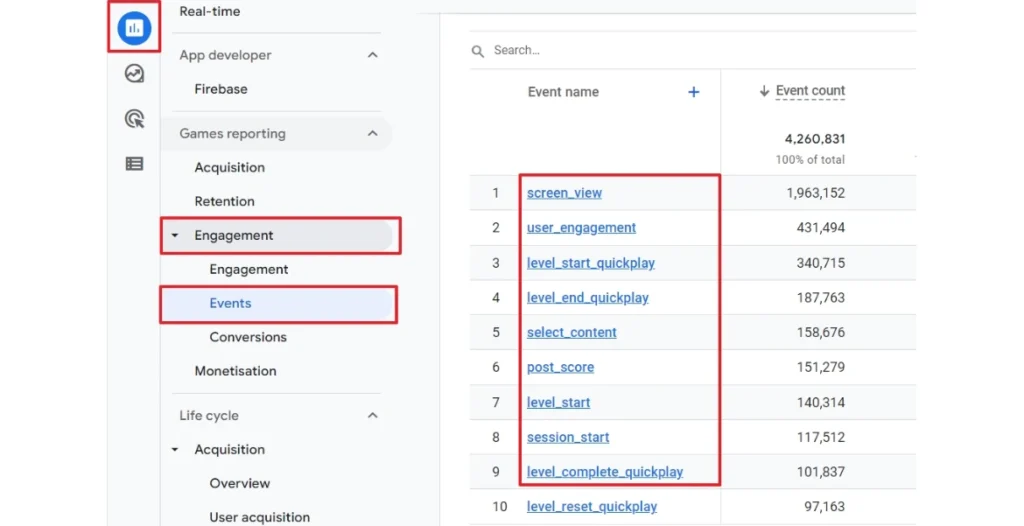
Suggested and Custom Events
For more specialized tracking, Google recommends certain events like purchases or video starts, but you can also set up custom events tailored to your needs. Custom events allow you to track unique actions that are specific to your business or website.
How Event Tracking Works in GA4?
With the advent of GA4, event tracking has become more flexible and comprehensive, enabling you to monitor interactions with greater precision.
Understanding Event Parameters
In GA4, each event comes with parameters that provide extra information about the interaction. For example, if you track video plays, parameters like the video title or duration can offer deeper insights into user behavior.
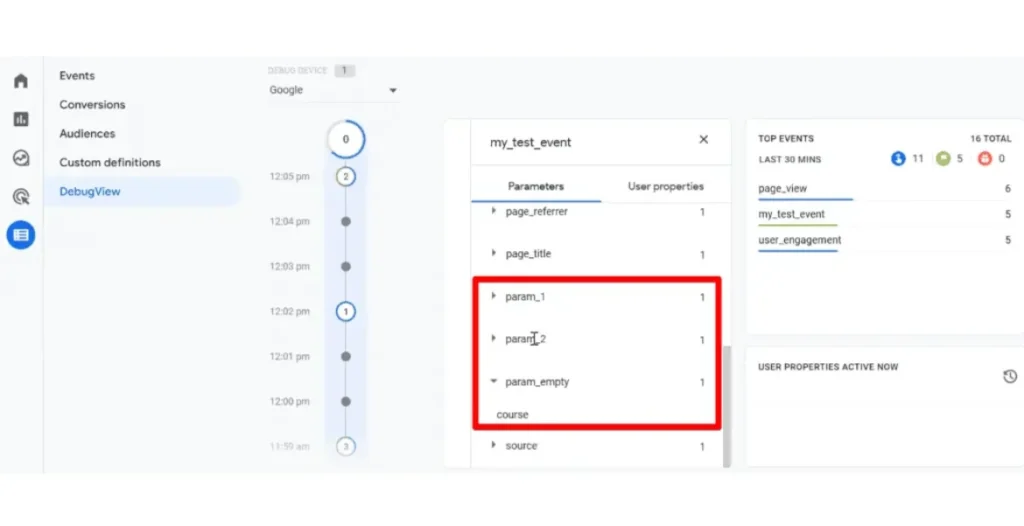
The Role of Values in User Behavior Tracking
You can assign values to different events to measure their importance. For instance, a user completing a purchase may be more significant than someone clicking a link. Setting these values helps prioritize interactions based on their relevance to your business goals.
Comparing Event Count with Total Events
Event count tracks individual user actions, while total events provide a cumulative sum of all event types. Grasping this difference is vital for:
- Precise analysis and decision-making
- Identifying trends and patterns
- Optimizing user engagement and conversion
Real-World Use Cases for Event Tracking
- Clicks on Buttons
Monitoring button clicks, especially on critical buttons like “Buy Now” or “Submit,” is essential for understanding user behavior and improving conversion rates.
- Form Submissions
Tracking how often users submit forms gives you insights into lead generation or sales, providing valuable data for improving your forms.
- Video Interaction Monitoring
For websites that feature video content, tracking how users engage with videos—such as play, pause, and completion rates—can help you refine your multimedia strategy.
Configuring Event Tracking in Google Analytics 4
GA4 provides an intuitive interface for setting up tailored events to track unique user behaviors.
Step 1: Create Events: In GA4, navigate to “Events” under “Configuration” and click “Create Event”. Define your event name, parameters, and conditions.
Step 2: Set Event Parameters: Add relevant parameters (e.g., event category, action, label) to capture detailed information about user interactions.
Step 3: Configure Event Triggers: Specify the conditions under which the event will fire, such as page loads, clicks, or form submissions.
Step 4: Assign Event Values: Optionally assign monetary values to events to measure revenue impact.
Step 5: Validate Event Tracking: Use GA4’s DebugView or Preview mode to verify events are firing correctly.
Step 6: Publish Changes: Save and publish your event tracking configuration to start collecting data.
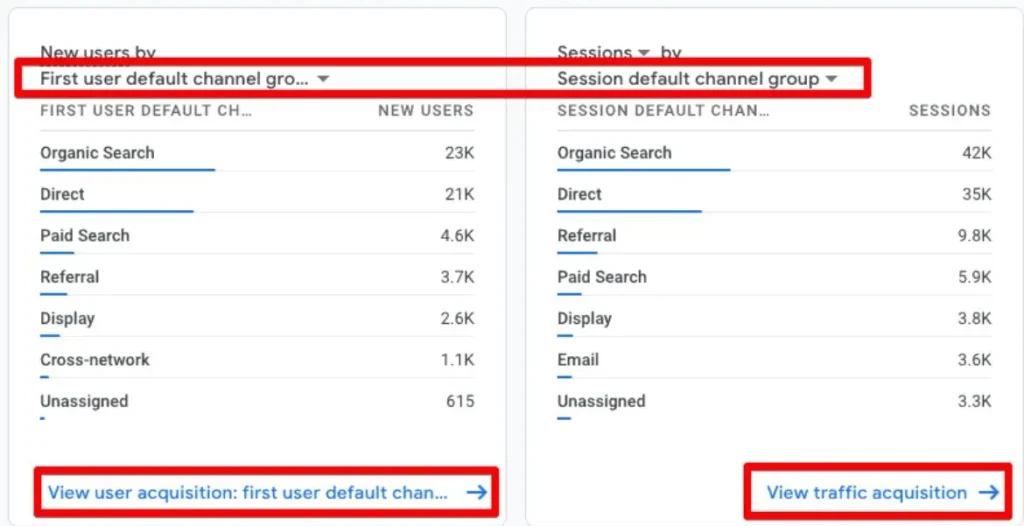
Accessing and Using Event Reports in GA4
After configuring your events, you can access detailed reports to analyze the data.
Locating Event Data
In GA4, you can find event reports under the “Reports” tab, providing a breakdown of event counts and other important metrics.
Using Reports to Interpret User Behavior
By analyzing these reports, you can gain valuable insights into how users interact with your content and identify trends that can help improve website performance.
Comparing Event Count with Other Metrics
Here’s how event count compares with other essential metrics in Google Analytics:
Event Count vs Session Count
Sessions measure the number of visits to your website, while event counts reflect the actions taken during those visits. Multiple events can occur during a single session. By tracking both, you gain insight into user engagement and behavior, revealing opportunities to optimize user experience and conversion rates.
Event Count vs Conversion Count
Event counts track all interactions on your website or app, while conversion counts focus on those specific actions that drive meaningful outcomes, such as:
- Event Count: Total number of interactions (e.g., clicks, views, swipes)
- Conversion Count: Number of goal-completing actions (e.g., purchases, sign-ups, downloads)
By monitoring both, you can optimize user journeys and enhance overall conversion rates.
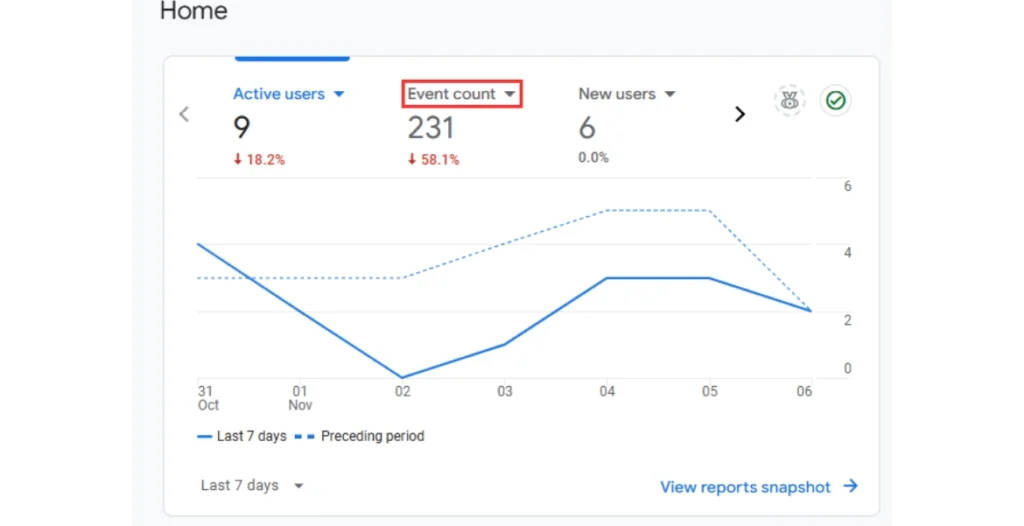
How Event Counts Relate to Views?
In many cases, the event count will exceed the number of page views, as multiple actions can take place within a single view. For example, a user may load a page once but trigger several events, such as clicks or form submissions.
Common Challenges with Event Tracking
Event Overcounting
Event overcounting occurs when the same event is triggered multiple times due to improper setup, resulting in:
- Double-counting of single actions
- Inflated event totals
- Skewed analytics and decision-making
To avoid this, ensure:
- Unique event IDs for distinct actions
- Clear event triggers and conditions
- Regular auditing of event tracking configurations
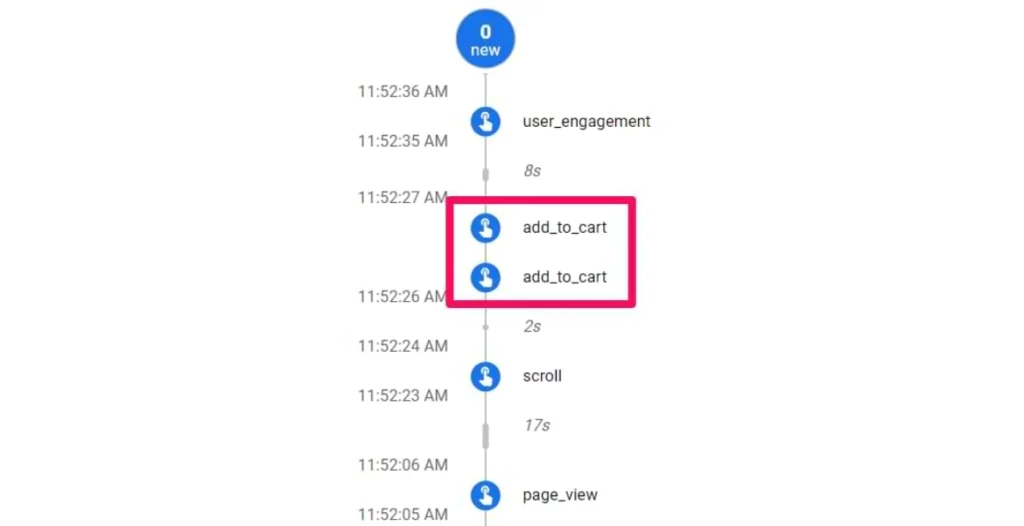
Duplicate Events
Duplicate events occur when an event is tracked more than once, often due to misconfiguration, resulting in:
- Inflated event counts
- Distorted data
- Compromised analytical insights
To mitigate this risk:
- Verify event tracking setup for uniqueness
- Use distinct event names and IDs
- Regularly audit event tracking configurations
Best Practices for Event Tracking
- Always define meaningful events that align with your business objectives.
- Verify event tracking integrity through frequent assessments.
- Use descriptive event names and parameters for easier data interpretation.
Improving Accuracy in Event Counts
Filtering Data
Use filters to clean up your data by removing irrelevant or duplicate events, helping you maintain accurate event counts.
Avoiding Duplicate Events
Double-check your setup to ensure events aren’t being triggered multiple times for the same user action. Verify:
- Unique event IDs for distinct actions
- Clear event triggers and conditions
- Proper event tracking configuration
Learn how Event Count enhances your website’s performance!
Let our experts explain how Event Count improves your GA4 insights!
Conclusion: The Significance of Event Tracking
Event counts are crucial for understanding user interactions beyond basic page views. By tracking these events accurately, you can make informed decisions that improve your site’s engagement and conversion rates.If you need expert help with event tracking, Go SEO Monkey offers tailored solutions for all your Google Analytics and
FAQs
- What is an event count?
An event count measures how often a specific user action occurs on your website. - How is event count different from page views?
Page views track how often a page is loaded, while event counts track specific interactions like clicks or form submissions. - Can I set up custom events in GA4?
Yes, GA4 allows you to create custom events tailored to track unique user actions. - Why might my event count exceed my session count?
It’s normal for event counts to be higher than session counts since multiple events can occur within a single session. - How can I prevent duplicate events?
Regularly review your event tracking setup to ensure each event is only tracked once per user action.





