Table of Contents
ToggleCookies are everywhere on the web, and if you’ve ever browsed a site that tracks user behavior, you’ve likely encountered them. In this expert breakdown, we’ll examine cookies’ role in Google Analytics, and provide actionable advice on navigating GDPR regulations and cookie consent best practices. Whether you’re a website owner or just curious about web analytics, this comprehensive guide will cover all the bases.
What Are Cookies?
Tiny text-based identifiers, or cookies, are saved on your device by websites to enhance navigation and customization. These files empower websites to recognize and respond to your unique preferences, streamlining your browsing sessions.
Discover what cookies are and how they affect your online privacy.
Unlock the mystery of cookies! Our experts guide you through their impact on your online experience.
Types of Cookies
Cookie classification simplifies into two main groups, isolating first-party and third-party cookies:
First-Party Cookies
First-party cookies, set by the website itself, enhance your browsing experience with targeted features and preferences. They help enhance user experience by remembering login information, language preferences, and other customizations.
Third-Party Cookies
These cookies come from other domains, often advertisers or analytics services, and track your browsing habits across multiple websites. They’re primarily used for targeted advertising and tracking user behavior.
The Role of Cookies in Google Analytics
How Google Analytics Uses Cookies?
Google Analytics relies heavily on cookies to collect data about user interactions on websites. When a user visits a site equipped with Google Analytics, the service places cookies on their device. These cookies track various metrics like page views, time spent on the site, and conversion rates, providing valuable insights into user behavior.
Common Cookies Used by Google Analytics
Google Analytics employs several cookies, each serving a specific purpose. Some of the most common and essential cookies are:
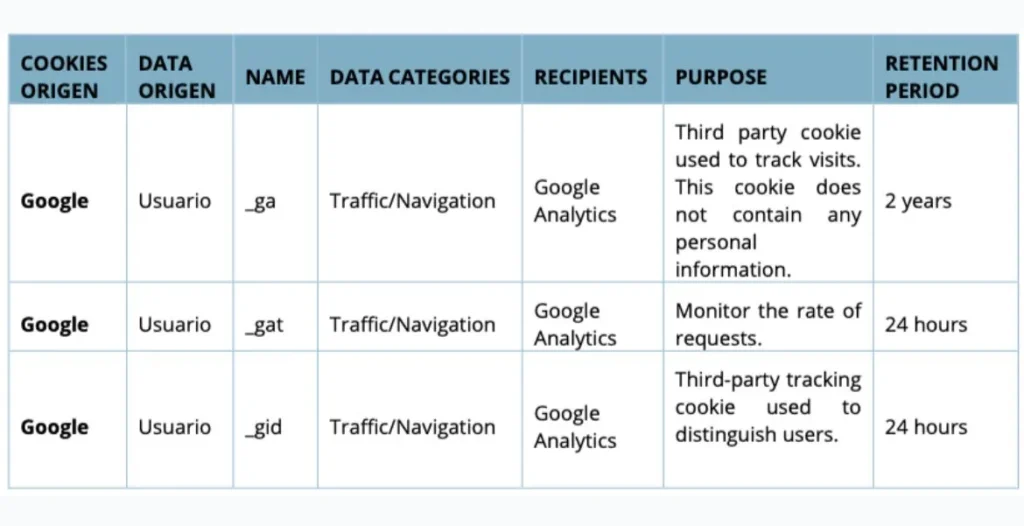
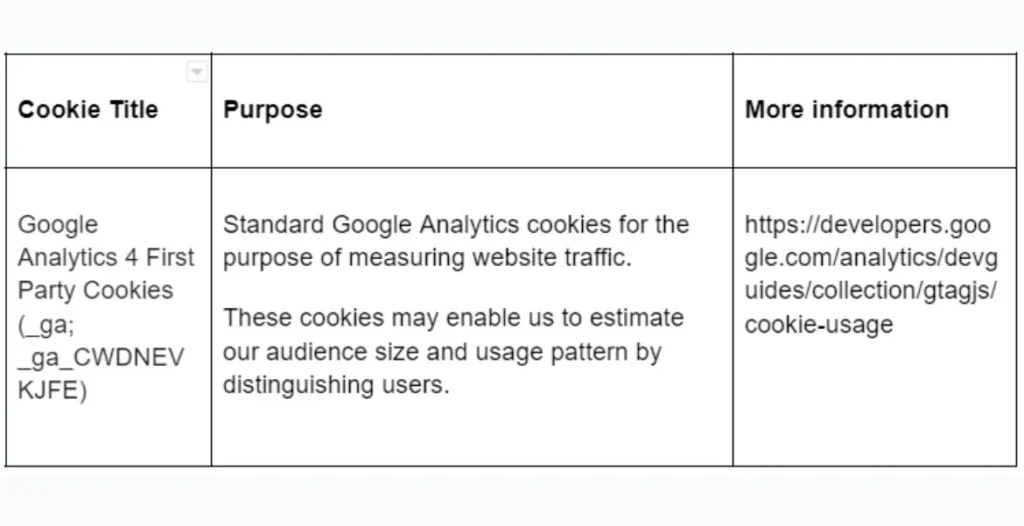
_ga Cookie
This cookie helps identify users and distinguishes them from one another. It’s important to track visitors’ behavior on your site.
_gid Cookie
Similar to the _ga cookie, the _gid cookie is used to store information about how users interact with the site, allowing Google Analytics to generate reports on website performance.
_gat Cookie
This _gat Cookie helps balance data collection efficiency with server capacity, preventing overload and ensuring uninterrupted analytics.
Cookie Consent and Google Analytics
1. What is Cookie Consent?
Cookie consent protocols allow users to opt-in or opt-out of data tracking, promoting online transparency.With increasing concerns about privacy, many regions have enacted laws that require websites to obtain explicit consent before utilizing cookies for data collection or tracking purposes.
2. Importance of Cookie Consent for Websites
Transparency in cookie usage cultivates user confidence, establishing a foundation for a trustworthy online relationship. When visitors understand what data is collected and how it’s used, they’re more likely to engage with your site.
3. How to Implement Cookie Consent?
- Cookie Banner Setup
A cookie banner is a pop-up that informs users about cookie usage and provides options to accept or reject cookies. Precise configuration is key to fostering a secure, intuitive, and compliant online environment.
- Cookie Policy for Google Analytics
Your website should have a clear cookie policy outlining which cookies are used, their purpose, and how users can manage their preferences. This transparency is vital for building trust and ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR.
How Cookies Send Data to Google Analytics?
1. Initiating a Website Visit
When a user opens a webpage that incorporates Google Analytics, their web browser begins the process by sending a request to load the page. This action activates the embedded Google Analytics tracking script.
2. Generating Cookies
Upon executing the tracking script, a unique cookie is created and stored on the user’s device. This cookie serves as an identifier for the specific user, allowing Google Analytics to distinguish between different visitors.
3. Collecting Interaction Data
The cookie plays a vital role in gathering a variety of information regarding the user’s engagement with the site. Key data points collected include:
- Page Views: It records each new page the user visits during their session.
- Time Spent: The cookie tracks how long the user remains active on the website.
- User Actions: It captures specific interactions, such as button clicks, form submissions, and video plays.
4. Sending Data to Google Analytics Servers
After collecting relevant data, the cookie facilitates the transmission of this information to Google Analytics servers. This process typically happens immediately or shortly after the user leaves the page.
The data package sent may include:
- Client ID: A distinctive identifier associated with the user’s cookie.
- Current Page URL: The web address of the page being accessed.
- Access Time: The timestamp indicating when the interaction occurred.
- Referring URL: The address of the previous page or site from which the user arrived.
5. Processing the Data
Once Google Analytics receives the information, it processes it to create meaningful reports and analytics. This step allows website owners to gain insights into how visitors use their site.
6. Ensuring Privacy Through Anonymization
To protect user privacy, Google Analytics anonymizes the data. This step ensures that no personally identifiable information is transmitted, keeping individual users’ identities confidential.
7. Accessing Analytical Insights
Website owners can log into the Google Analytics dashboard to view detailed reports based on the data collected through cookies. This information is instrumental in understanding user behavior, identifying traffic sources, and improving website performance.
Learn how cookies transmit data to Google Analytics today!
Our experts simplify how cookies relay data to Google Analytics for better insights!
Google Analytics Without Cookies
Is it Possible to Use Google Analytics Without Cookies?
Yes, it’s possible to use Google Analytics in a cookie-less mode, but with limitations. While you can still track some data, you may lose the granularity and insights cookies provide.
Alternatives to Cookies for User Tracking
Some alternatives include using local storage or server-side tracking. However, these methods may require a different setup and come with their challenges.
Cookie Expiration
Cookie expiration refers to the time period after which a cookie stored in a user’s browser is considered invalid and is automatically deleted. This mechanism helps manage the data stored and ensures that outdated information does not linger on users’ devices.
1. How Cookie Expiration Works?
When a cookie is created, it is assigned an expiration date. Once this date is reached, the browser removes the cookie from the user’s device, and it can no longer be accessed by the website. Expiration dates can be set during cookie creation by specifying a “Max-Age” or “Expires” attribute.
2. Types of Cookie Expiration
Session Cookies:
These cookies expire once the user closes their browser. They are used for temporary storage, like keeping a user logged in during a single browsing session.
Persistent Cookies:
These cookies remain on the user’s device for a specified duration or until the user manually deletes them. They are useful for remembering user preferences and login information across sessions.
3. Typical Duration for Google Analytics Cookies
Google Analytics cookies generally have a lifespan of two years. However, the specific expiration time can vary depending on the type of cookie:
- _ga Cookie:
Expires after 2 years.
- _gid Cookie:
Expires after 24 hours.
- _gat Cookie:
Expires after 1 minute.

4. Importance of Setting Expiration Dates
Setting appropriate expiration dates is crucial for several reasons:
- Data Management: Helps manage storage on user devices, preventing excessive accumulation of outdated cookies.
- Privacy Considerations: Reduces the risk of retaining potentially sensitive data longer than necessary, enhancing user privacy.
- Accuracy of Analytics: Ensures that the data collected reflects current user interactions, providing more accurate insights for website owners.
5. User Control Over Cookie Expiration
Users can manage cookie expiration through their browser settings:
- Delete Cookies: Users can manually remove cookies, which also deletes those that have not yet expired.
- Adjust Settings: Browsers often provide options to block certain cookies or limit their lifespan, giving users more control over their privacy.
6. Impact of Expiration on User Experience
Expiration of cookies can affect user experience in various ways:
- Login Sessions: Users may find themselves logged out of websites if session cookies expire unexpectedly.
- Saved Preferences: Users might need to reset their preferences if persistent cookies have expired, which can be inconvenient.
Cookies and GDPR Compliance
Understanding GDPR and Its Impact on Cookie Usage
The GDPR constitutes a comprehensive regulatory overhaul, fortifying individual rights and organizational responsibilities regarding data handling.It requires that businesses collect explicit consent from users before using cookies that track personal data.
How to Ensure Compliance with GDPR?
Best Practices for Cookie Consent
- Be Clear and Concise: Make sure your cookie consent banner is straightforward, detailing what cookies are used and their purposes.
- Provide Options: Users should have the ability to accept or decline non-essential cookies.
- Keep Records: Maintain a record of user consents to demonstrate compliance if needed.
User Rights and Cookie Management
GDPR safeguards individuals’ autonomy by granting them the right to access, modify, or expunge their personal data. It’s essential to inform users about how they can manage their cookie preferences and exercise their rights.
Stay GDPR compliant—get expert guidance for your business!
Achieve peace of mind with our tailored GDPR compliance strategies!
Conclusion
Understanding how cookies work with Google Analytics is essential for website owners and marketers alike. By implementing cookie consent properly and ensuring GDPR compliance, you can build trust with your audience while gaining valuable insights into their behavior.
If you’re looking for professional assistance in managing your website’s analytics and ensuring compliance with cookie policies, consider reaching out to Go SEO Monkey. Our team is here to help you navigate the complex world of web analytics and privacy regulations.
FAQs
- What cookies does Google Analytics use?
Google Analytics primarily uses _ga, _gid, and _gat cookies to track user interactions on websites. - How can I change cookie settings in Google Analytics?
You can manage cookie settings through the Google Analytics interface and ensure your cookie banner provides options for user consent. - What happens if I don’t give cookie consent?
If you do not provide cookie consent, the website may limit certain functionalities, such as tracking your interactions for analytics purposes. - Are there any privacy concerns with Google Analytics cookies?
While Google Analytics is designed to protect user privacy, there are concerns regarding data collection and user tracking. Implementing cookie consent policies can help mitigate these concerns. - How often are Google Analytics cookies updated?
Google Analytics cookies are updated every time a user interacts with the website, allowing for real-time data tracking and reporting.





