Table of Contents
ToggleGoogle Analytics is an invaluable tool for understanding website traffic, user behavior, and overall performance. However, without proper data filtering, your reports might be cluttered with irrelevant or misleading information. This is where filters come in, helping you refine data to gain actionable insights. So, what are the options for filtering data in Google Analytics? Let’s dive in!
Filters in Google Analytics are rules or conditions applied to your data to modify, include, or exclude specific information. They ensure your reports reflect only the data you care about, enhancing accuracy and relevance.
Types of Filters in Google Analytics
- Predefined Filters
These are built-in filters designed for common data needs. They’re straightforward to set up and ideal for basic filtering tasks like excluding internal traffic or targeting specific domains.
- Custom Filters
Want more control? Custom filters enable personalized rule creation to meet distinct needs. For example, you can filter data based on user demographics, behaviors, or even custom dimensions.
Discover Google Analytics data filtering options now!
Let our experts guide you in mastering GA data filtering for actionable insights!
Do you want to apply filters in Google Analytics?
Setting Up Custom Filters in GA: Step-by-Step Guidelines
- Log in to Your Google Analytics Account – Start by accessing your GA account and selecting the property where you want to set up filters.
- Open the Admin Section – On the bottom-left side of the dashboard, click the Admin gear icon.
- Choose the Desired Account – Under the Account column, select the account you’re working on.
- Access the Filters Option – In the View column, click on Filters to manage or create new filters.
- Add a New Filter – Click the + Add Filter button to begin setting up a new custom filter.
- Name Your Filter – Enter a unique and descriptive name to identify the filter easily.
- Select a Filter Type – Choose either Predefined Filter or Custom Filter, depending on your filtering needs.
- Set Up Filter Details – For custom filters, specify the filter field (e.g., IP address, hostname) and define the pattern or conditions.
- Assign Views to the Filter – Select the specific views where the filter should be applied.
- Save Your Filter Settings – Click the Save button to apply the new filter to your selected views.
Each step ensures your custom filters are configured accurately, allowing for refined data analysis tailored to your business needs.
Key Filtering Options in Google Analytics
Filters in Google Analytics (GA) are essential for refining and segmenting your data, allowing you to focus on what’s most relevant to your business. Let’s dive deeper into some key filtering options and their applications:
Include and Exclude Filters
These filters are crucial for narrowing down or eliminating specific datasets from your reports.
- Include Filters: These focus on specific data that meets your criteria. For example, if you want to analyze traffic from a particular country, you can create an include filter for that location.
- Exclude Filters: These remove unwanted data from your reports. For instance, excluding internal traffic from your company’s IP ensures that employee visits don’t distort your user metrics.
Steps to Set Up Include/Exclude Filters
- Navigate to Filters in the Admin section under the View column.
- Click + Add Filter and provide a filter name.
- Select Predefined Filter and choose Include or Exclude.
- Define the field (e.g., IP address, geographic location) and set your conditions.
- Save the filter.
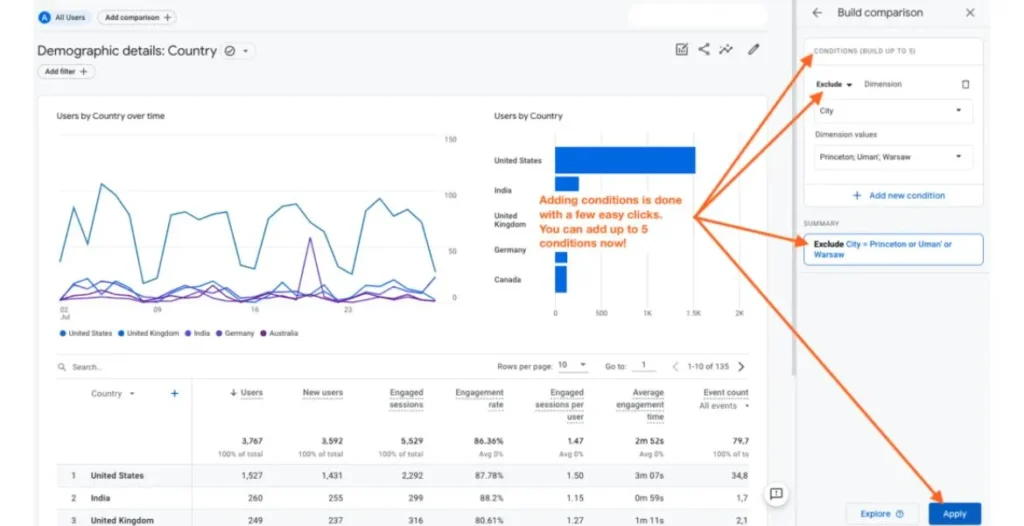
Lowercase and Uppercase Filters
Data inconsistencies can affect your reports, especially when case sensitivity comes into play. For instance, “Homepage” and “homepage” may be treated as separate entities in GA.
- Lowercase Filters: Convert all data within a specific field to lowercase.
- Uppercase Filters: Convert all data to uppercase, ensuring uniformity.
These filters are commonly used for URLs, page titles, and campaign parameters, helping to eliminate duplication and standardize your dataset.
Steps to Apply Lowercase/Uppercase Filters
- Navigate to Filters and select ‘Add Filter’.
- Choose Custom Filter and select either Lowercase or Uppercase.
- Specify the field you want to standardize (e.g., Request URI, Campaign Name).
- Save your changes.
Search and Replace Filters
- Example Use Case: You have URLs with long query strings like
example.com/page?id=123&session=abc. Using a Search and Replace filter, you can replace the long query string with a simpler term likeexample.com/page. This makes your reports cleaner and easier to analyze.
- Open the Filters section in the Admin panel.
- Add a new filter by clicking ‘+’ and provide a detailed name.
- Choose Custom Filter type and select Search/Replace.
- Identify the field to edit (e.g., Request URI).
- Enter the Search and Replace strings.
- Save your filter.
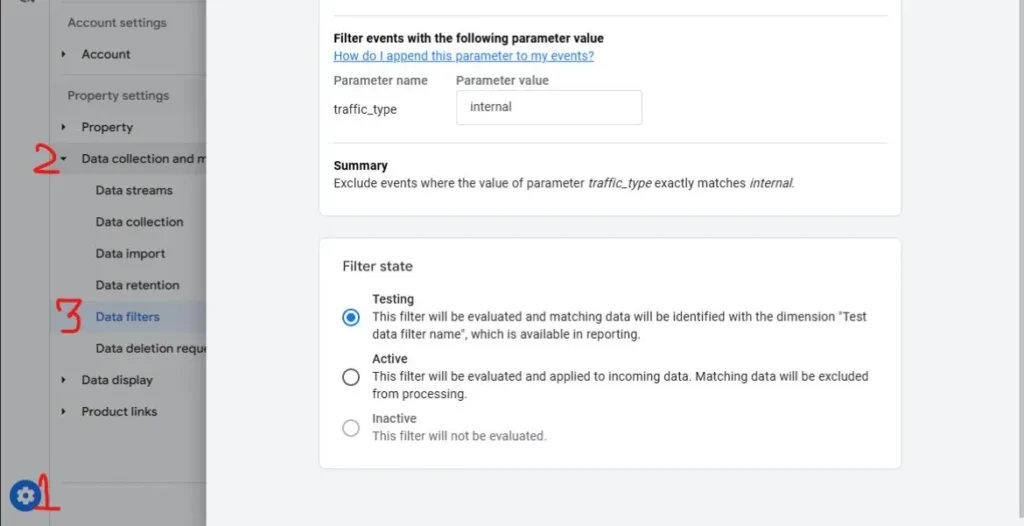
Why These Filters Matter?
Each filter type plays a specific role in ensuring that your GA data is clean, accurate, and relevant. By using them effectively, you can focus on actionable insights, reduce noise, and make better business decisions.
Using Regular Expressions (Regex) in Filters
If you’re dealing with complex data patterns, Regex is your best friend. It allows you to create dynamic filters for nuanced data segmentation, like capturing multiple variations of a URL. Regex enables precise matching, simplifying complex filtering tasks. Its flexibility facilitates efficient data analysis and segmentation. Effective Regex application streamlines filter creation.
Applying Filters to Views
Filters can be applied to specific views within Google Analytics to tailor your reports. This ensures each team or stakeholder sees data relevant to their goals without interference. By segmenting data, teams focus on key metrics. Customized views enhance decision-making. Targeted insights promote strategic alignment.
Understanding Filter Order and Its Impact
The sequence in which filters are applied matters. Filters are processed in the order they’re listed, so a poorly structured sequence could lead to inaccurate data. For example, an exclude filter applied before an include filter might inadvertently remove desired data.
Best Practices for Filtering Data
- Test Before Applying: Always preview your filters to ensure they work as expected.
- Avoid Overfiltering: Too many filters can distort your data, so apply only what’s necessary.
Advanced Filtering Techniques
- Geographic and Language Filters
These filters let you analyze traffic based on location or language. Want to see how users from Japan interact with your site? These filters make it possible.
- Traffic Source Filters
Understand where your traffic comes from by filtering data by source. Whether it’s organic search, direct traffic, or social media, source filters provide valuable segmentation.
Tools to Complement Google Analytics Filtering
Google Tag Manager is a great companion for advanced filtering needs. Additionally, third-party tools can integrate with Google Analytics for even more robust data management. These integrations enhance filtering capabilities. They offer specialized features like automated data cleanup and advanced segmentation. Integrated workflows streamline data analysis. Precision filtering enables informed decision-making.
Common Issues with Data Filtering
Misconfigured filters can wreak havoc on your data. Whether it’s accidentally excluding critical data or applying filters in the wrong order, it’s essential to test and troubleshoot regularly. Inconsistent filtering leads to inaccurate insights. Regular audits prevent data discrepancies. Proactive maintenance ensures reliability.
Find out the best ways to filter data in GA today!
Our specialists make data filtering in GA simple and impactful for your business!
Conclusion
Filtering data in Google Analytics is like cleaning your glasses—you won’t see clearly without it. By using the options outlined above, you can ensure your data is accurate, actionable, and aligned with your goals. If you need help optimizing your data filtering strategies, Go SEO Monkey offers expert services to take your analytics to the next level.
FAQs
- What are predefined filters in Google Analytics?
Predefined filters are built-in options designed to handle common filtering tasks, such as excluding internal traffic or targeting specific domains. - How do custom filters differ from predefined ones?
Custom filters allow for more flexibility, enabling you to define specific rules tailored to your unique data analysis needs. - Can filters be applied retroactively?
No, filters only affect data collected after their implementation. Historical data remains unchanged. - How can I test my filters before applying them?
Google Analytics provides a filter preview option, letting you see how your data will look without permanently altering it. - What are some common mistakes to avoid when filtering data?
Common pitfalls include applying filters in the wrong order, using overly restrictive filters, and failing to test filters before use.





