Table of Contents
ToggleWhen diving into the world of e-commerce analytics, one term you’ll frequently encounter is Average Order Value (AOV). This metric plays a crucial role in understanding your customers’ purchasing habits and can significantly impact your overall revenue strategy.
If you’re looking to learn how to find AOV in Google Analytics 4 (GA4), you’re in the right place! This article will guide you through everything you need to know, from the fundamental concepts of AOV to step-by-step instructions on how to analyze it effectively within GA4.
What is Average Order Value (AOV)?
Average Order Value, or AOV, is a metric that measures the average amount of money each customer spends per transaction. Calculating AOV helps businesses understand their revenue potential and customer buying behavior.
Why should you care about AOV? Well, increasing your AOV means boosting your revenue without necessarily increasing your customer base. It’s like finding a hidden gem in your store—enhancing what you already have instead of starting from scratch!
You are only a step away from skyrocketing your business!
Analytics can help optimize your website to generate leads like never before. Set up analytics with GSM.
Key Metrics Related to AOV
- Total Revenue: This is the overall income generated from sales. Monitoring total revenue alongside AOV helps you assess the financial health of your e-commerce business.
- Total Number of Orders: This metric represents the total count of transactions during a specific period. It’s essential for calculating AOV and understanding customer purchasing frequency.
- Conversion Rate: This measures the percentage of visitors who make a purchase. A higher conversion rate often correlates with an increased AOV, indicating effective marketing and product offerings.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): CLV estimates the total revenue a customer will generate over their entire relationship with your business. Understanding CLV alongside AOV can help you develop strategies to retain high-value customers.
- Cart Abandonment Rate: This metric tracks the percentage of shoppers who add items to their cart but leave without completing the purchase. Reducing abandonment can directly increase both total orders and AOV.
- Return Rate: This measures the percentage of products returned by customers. A high return rate can negatively impact AOV, indicating potential issues with product quality or customer satisfaction.
- Revenue per Transaction: Similar to AOV, this metric focuses on revenue generated from individual transactions. Analyzing this alongside AOV can provide insights into customer spending behavior.
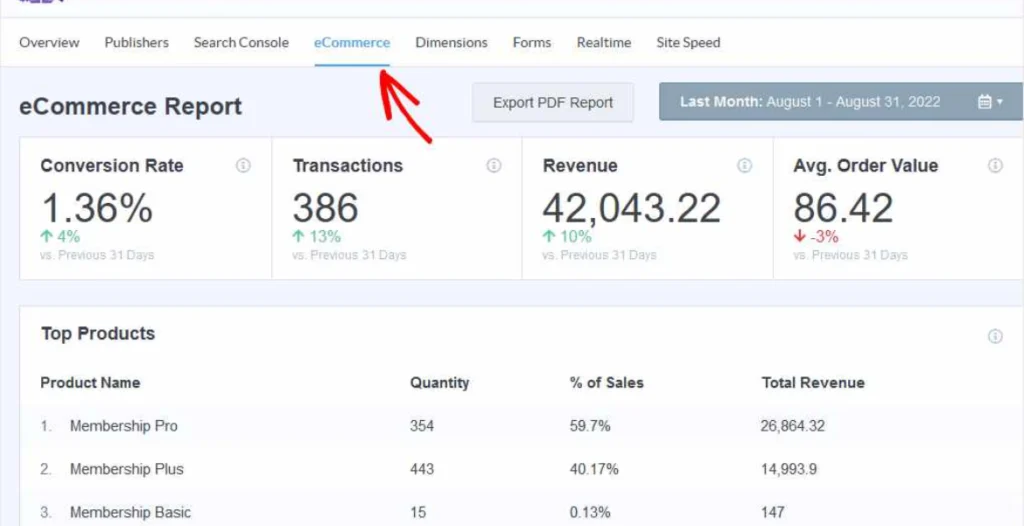
Setting Up GA4 for E-commerce Tracking
- Create a GA4 Property:
- Log in to your Google Analytics account.
- Click on “Admin” in the lower-left corner.
- In the “Property” column, click “Create Property” and follow the prompts to set up a GA4 property.
- Add a Data Stream:
- Under your newly created GA4 property, select “Data Streams.”
- Click on “Add Stream” and choose “Web” for a website or “App” for a mobile application.
- Enter your website URL and stream name, then click “Create Stream.”
- Enable Enhanced E-commerce:
- In the Data Stream settings, locate the “Enhanced Measurement” section.
- Toggle the switch to enable enhanced measurement features.
- Ensure options like “Page views” and “Scrolls” are activated for comprehensive tracking.
- Set Up E-commerce Events:
- Implement the necessary e-commerce events on your website using Google Tag Manager (GTM) or directly in your code.
- Key events include:
view_item: Tracks product views.add_to_cart: Monitors items added to the cart.begin_checkout: Records the start of the checkout process.purchase: Captures completed transactions.
- Refer to the GA4 E-commerce documentation for specific parameters and implementation details.
- Configure Event Parameters:
- For each event, ensure you include relevant parameters, such as:
item_name: Product name.item_category: Product category.price: Product price.quantity: Number of items purchased.
- This data is crucial for detailed reporting.
- For each event, ensure you include relevant parameters, such as:
- Verify Data Collection:
- Use the GA4 DebugView to check if events are firing correctly.
- In GA4, navigate to “Configure” > “DebugView” and perform test actions on your site (like adding items to the cart).
- Ensure the relevant events appear in real time.
- Set Up Conversion Tracking:
- In GA4, mark key events (like
purchase) as conversions. - Go to “Configure” > “Conversions” and click “New conversion event.”
- Enter the name of the event you want to track as a conversion.
- In GA4, mark key events (like
- Link GA4 to Google Ads (if applicable):
- If you’re using Google Ads, link your GA4 property for better insights.
- In the “Admin” section, go to “Product Linking” and select “Google Ads.”
- Follow the prompts to complete the linking process.
- Review Reporting Settings:
- Navigate to the “Reports” section to explore e-commerce metrics.
- Check under “Monetization” to see reports related to e-commerce performance, including revenue and AOV.
- Regularly Monitor and Optimize:
- Schedule regular reviews of your GA4 reports to track performance.
- Use insights gained to refine your marketing strategies, improve product offerings, and optimize the customer experience.

Navigating GA4 Interface to Find AOV
- Log into GA4:
- Go to the Google Analytics website and log into your account.
- Select the GA4 property you set up for your e-commerce site.
- Access the Reports Section:
- In the left-hand menu, click on “Reports.” This section provides an overview of your site’s performance, including e-commerce metrics.
- Locate the Monetization Tab:
- Within the Reports section, find the “Monetization” tab.
- Click on it to access reports specifically related to revenue and e-commerce performance.
- View E-commerce Purchases Report:
- Under the Monetization tab, select “E-commerce purchases.”
- This report shows key metrics related to purchases, including total revenue, number of purchases, and AOV.
- Analyze the AOV Metric:
- In the E-commerce purchases report, look for the Average Order Value (AOV) metric.
- This is typically displayed alongside other important metrics like total revenue and total orders.
- Use Date Comparisons:
- At the top right of the report, use the date range selector to compare AOV over different periods (e.g., last 7 days vs. last 30 days).
- This helps identify trends and fluctuations in AOV over time.
- Apply Filters:
- Use filters within the report to segment data by product category, traffic source, or other dimensions.
- This allows you to analyze AOV across different customer segments or marketing channels.
- Explore Secondary Dimensions:
- Click on the “Add comparison” button to explore secondary dimensions, such as user demographics or device categories.
- This provides deeper insights into which customer groups contribute to higher AOV.
- Export Data for Further Analysis:
- If needed, export the report data by clicking the export icon (usually found at the top right).
- Choose a format (CSV, Excel, PDF) to analyze the data in your preferred tool.
- Set Up Custom Reports (if necessary):
- For more tailored insights, consider creating custom reports.
- In the “Explore” section, click on “Create a new exploration” to build a report focusing specifically on AOV and related metrics.
Calculating AOV in GA4
- Understand the AOV Formula:
- The formula for calculating Average Order Value (AOV) is:
AOV = Total Revenue / Total Number of Orders - This formula gives you the average amount spent by customers per transaction.
- The formula for calculating Average Order Value (AOV) is:
- Gather Total Revenue Data:
- In GA4, navigate to the “Monetization” section under “Reports.”
- Look for the Total Revenue metric in the “E-commerce purchases” report. This metric represents the total income from sales over your selected date range.
- Obtain Total Number of Orders:
- In the same report, locate the Total Purchases metric. This indicates the number of completed orders during the specified period.
- Make sure to note the timeframe you’re analyzing.
- Calculate AOV Using GA4 Data:
- Once you have both metrics, apply the AOV formula:
AOV = Total Revenue / Total Purchases - For example, if your total revenue is $10,000 and total purchases are 500, the AOV would be:
AOV = 10,000 / 500 = 20 - This means the average customer spent $20 per order.
- Once you have both metrics, apply the AOV formula:
- Check Historical AOV Data:
- To analyze trends, you can check AOV for previous periods.
- Use the date range selector to compare different timeframes (e.g., month-over-month or year-over-year).
- Segment AOV by Dimensions:
- Consider segmenting AOV by dimensions such as product category, traffic source, or customer demographics.
- This can help you identify which segments have higher or lower AOV, allowing for targeted marketing strategies.
- Use Google Sheets or Excel for Calculation:
- If you prefer, export the data to Google Sheets or Excel for further analysis.
- Use spreadsheet formulas to calculate AOV for different segments or timeframes easily.

Analyzing AOV Trends
Using GA4 to Analyze Purchase Events
GA4 provides robust tools for analyzing your purchase events. By diving into these reports, you can visualize how AOV changes over different time periods or across different customer segments.
Identifying Trends Over Time
Tracking AOV over time can reveal valuable insights into your business’s performance. Are there specific seasons where your AOV spikes? This knowledge can help you plan marketing strategies accordingly.
Improving AOV Through Strategy
Techniques to Boost AOV
Now that you understand how to find AOV, let’s discuss how to improve it. Here are a few effective strategies:
- Upselling and Cross-selling: Encourage customers to buy related products.
- Bundling Products: Offer discounts for purchasing items together.
- Loyalty Programs: Reward customers for higher spending.
Understanding Customer Behavior
Taking the time to analyze customer behavior can significantly affect your AOV. By understanding what your customers value, you can tailor your offerings to meet their needs and drive higher spending.
Boost Your AOV with GSM!
Go SEO Monkey can take care of boosting your AOV with their expertise and help boost your sales.
Conclusion
Finding and analyzing AOV in GA4 is not just about crunching numbers; it’s about gaining a deeper understanding of your customers and leveraging that knowledge to drive your business forward. By recognizing purchasing patterns and preferences, you can customize your offerings to better meet customer needs, ultimately enhancing their shopping experience.
If you’re looking for expert guidance in optimizing your e-commerce strategy, consider reaching out to Go SEO Monkey’s services. They offer custom support and expertise tailored to your specific business goals, helping you unlock your full revenue potential and navigate the complexities of online sales more effectively.
FAQs
- What does AOV mean in e-commerce?
AOV stands for Average Order Value, which measures the average amount spent by customers per transaction. - How do I calculate AOV in GA4?
AOV can be calculated using the formula: Total Revenue / Total Number of Orders. - Why is AOV important for my business?
AOV helps you understand customer spending behavior, enabling you to increase revenue without needing more customers. - How can I improve my AOV?
You can improve AOV through upselling, bundling products, and implementing loyalty programs. - What are some common pitfalls in calculating AOV?
Common pitfalls include misinterpreting data and ignoring the significance of customer segments.





